Making a difference on your farm


The SoilCQuest Soil Carbon Compass©

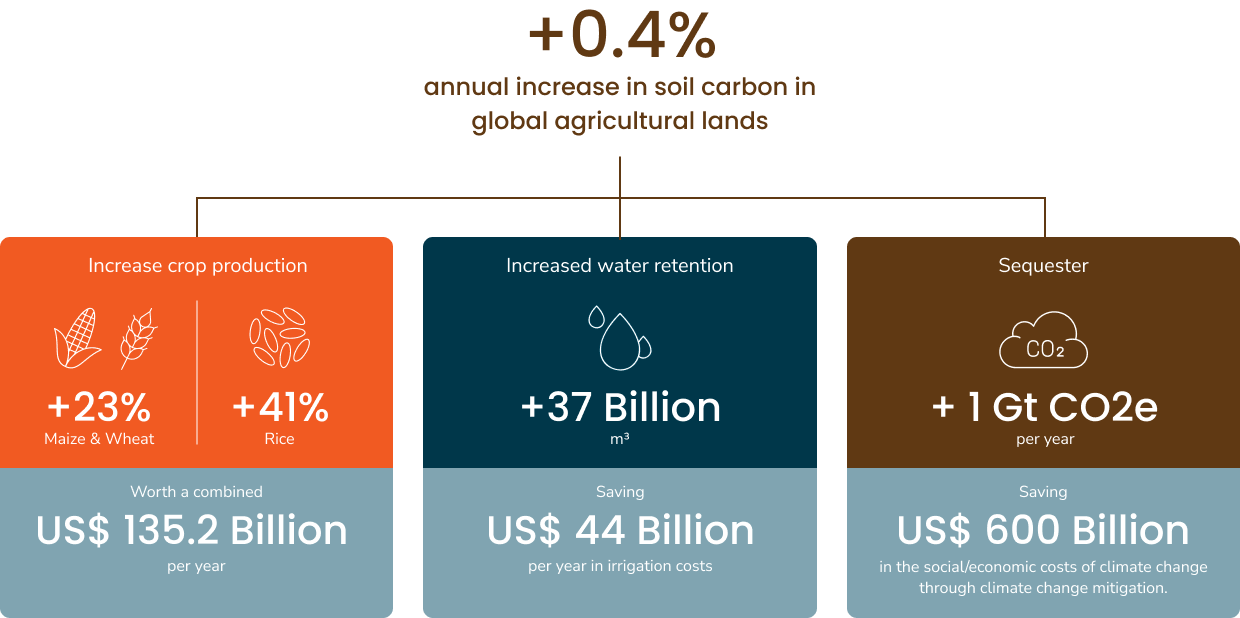
How more soil carbon would benefit agriculture and society
Nature’s free inputs
Managing above and below-ground biodiversity and the small water cycle allow farmers to harness the free inputs that nature provides.
Biodiversity
- Remnant Connection Connecting existing remnant vegetation incorporated as windbreaks & shelterbelts.
- Tree Lines creating biodiverse multispecies tree lines as strategic windbreaks & shelterbelts.
- Fodder Trees connecting remnant vegetation via fodder tree / shrub alleys as biodiversity connectivity.
- Paddock Perimeter & Block Plantings creating moisture trapping microclimates via vegetation paddock perimeters and internal paddock block plantings that host various native animals.
- Agroforestry & Hort Trees timber & fruit/nut treescreating ecological environments for biodiversity.
Avoided Deforestation
- Conserving remnant vegetation
- Feral Animal Control to protect native animals
- Exclusion fencing
- Strategic grazing for fire hazard reduction and understorey health
Water
Energy
Waste Management
Cropping
Conservation Farming
-
Min / zero till
-
Legume rotation
-
Stubble retention
-
Controlled traffic
-
Stripper fronts
Regenerative Farming
- Cover Cropping
- Intercropping
- Crimp Rolling
- Root Mass Stimulation
- One-Way-Valve Cover
- Fallows
Soil Carbon Inoculum
Crop specific soil carbon-fixing fungal inoculums.
Compost Applications
pH Soil Amendments
-
Lime
-
Gypsum
-
Dolomite
-
Rock Phosphate
Grazing
100% Groundcover, 100% of the time.
High stocking density with short grazing periods & long rest periods.
FAST Carbon- Fodder Alley Sequestration Trees
-
Tagasaste- Lucerne Tree
-
Leucaena- Sub tropical legume fodder shrub
-
Desmanthus- Fodder Legume shrub
-
SaltBush- Undersown & inter row seeded with hard seeded legume annuals & Lucerne
-
Kurrajong Fodder Tree- slow growing, long lived
-
Native Fodder Trees- Soil & environment specific, e.g. Mulga, Myall, Wilga, Wattle, Rosewood
Fodder & Grain
-
Time controlled grazing
-
Dual purpose multi-species fodder and grain crops
-
Pasture cropping
-
Perennial Multispecies Legume based
Methane Management
Feed additives

